Three way Switch Wiring Diagram
Understanding how to read and interpret a Three way Switch Wiring Diagram is essential for any DIY enthusiast or professional electrician. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical connections within a three-way switch circuit, allowing you to troubleshoot problems, make repairs, or install new switches with ease.
Why Three way Switch Wiring Diagrams are Essential
- Helps in understanding the electrical connections between switches and lights
- Ensures proper installation and wiring of three-way switches
- Aids in troubleshooting electrical issues within the circuit
- Provides a reference guide for future maintenance or repairs
Reading and Interpreting Three way Switch Wiring Diagrams
When looking at a Three way Switch Wiring Diagram, it’s important to pay attention to the following key components:
- Switches: Identify the positions of the switches (e.g. switch 1, switch 2)
- Wires: Note the color-coding and connections of the wires between switches and lights
- Terminals: Understand the terminal designations (e.g. common, traveler) on the switches
- Connections: Follow the lines to see how the switches and lights are interconnected
Using Three way Switch Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
When faced with electrical issues in a three-way switch circuit, a wiring diagram can be your best friend. By comparing the actual wiring to the diagram, you can quickly identify the problem areas, such as loose connections, faulty switches, or damaged wires. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
- Check for continuity between terminals using a multimeter
- Look for signs of overheating or burning on wires or switches
- Ensure proper grounding and insulation of wires
- Follow the diagram to trace the flow of electricity and pinpoint the source of the issue
Safety First!
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind when using Three way Switch Wiring Diagrams:
- Turn off the power before starting any electrical work
- Use insulated tools to prevent electric shock
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions
- Double-check all connections before restoring power
- If in doubt, consult a professional electrician
Three way Switch Wiring Diagram
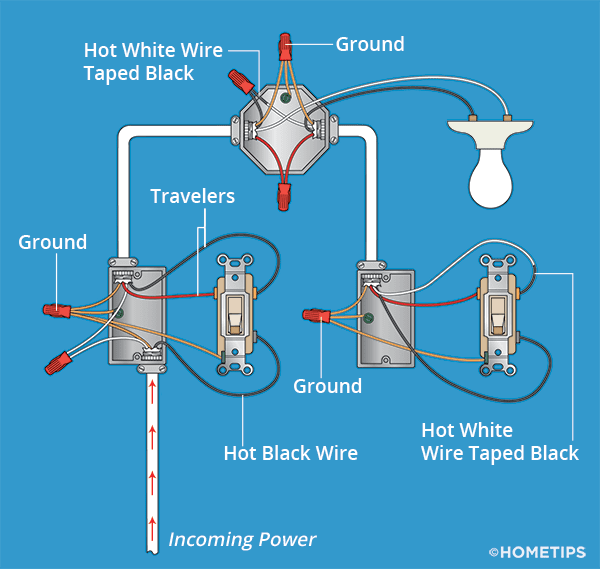
How to Wire Three-Way Light Switches | HomeTips
3-Way Switch Wiring Explained – MEP Academy

How to Wire a 3-Way Switch: Wiring Diagram – Dengarden

[Proper] 3 Way Switch Wiring and Connection Diagram – ETechnoG
![Three way Switch Wiring Diagram [Proper] 3 Way Switch Wiring and Connection Diagram - ETechnoG](https://i1.wp.com/1.bp.blogspot.com/-H_oNBfwZ_tM/XO7F94xoHCI/AAAAAAAAB8I/nLh7DyWH5ac2oahDDj_0wApr_pvBb7jkgCLcBGAs/s1600/3%2Bway%2Bswitch%2Bwiring%2Bconnection.png)
Three-way Switch Wiring Diagrams

3 way switch | How to wire a light switch
