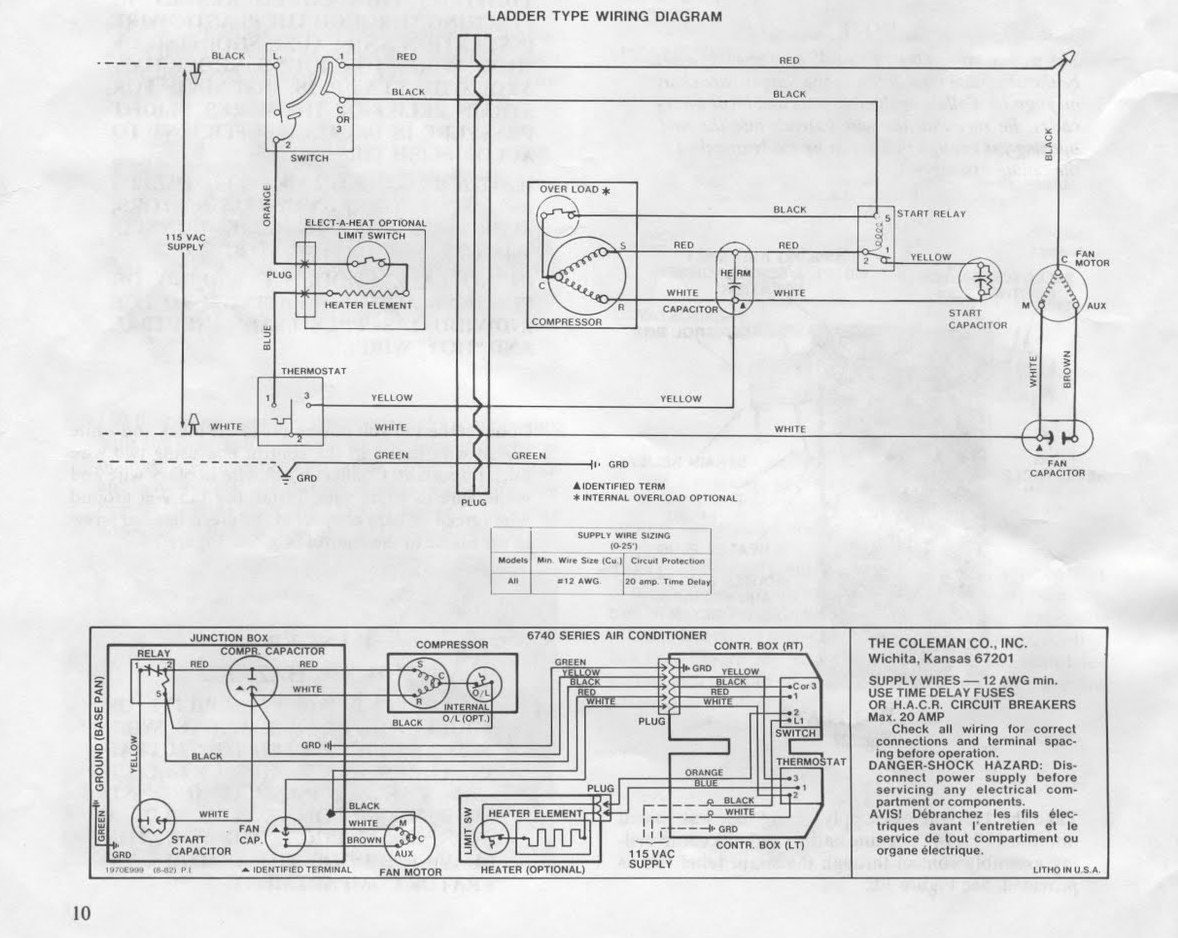
When it comes to understanding and fixing issues with your RV’s air conditioning system, having a clear and detailed RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagram can be incredibly helpful. This diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical connections within the AC unit, making it easier to identify problems and make repairs.
Why are RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams Essential?
RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams are essential for several reasons:
- They help you understand the electrical layout of your RV’s air conditioning system.
- They make it easier to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with the AC unit.
- They provide a roadmap for making electrical repairs or installations.
How to Read and Interpret RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams Effectively
Reading and interpreting RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams may seem daunting at first, but with some guidance, it can become much easier:
- Start by identifying the different components of the wiring diagram, such as the compressor, fan motor, thermostat, and power supply.
- Follow the lines and symbols to trace the electrical connections between the components.
- Pay attention to colors and labels to distinguish between different wires and circuits.
Using RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams are invaluable tools when it comes to troubleshooting electrical problems in your AC system:
- Refer to the diagram to locate the source of the issue, whether it’s a faulty connection, broken wire, or malfunctioning component.
- Use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage of different circuits and wires as indicated on the diagram.
- Follow the wiring diagram to make necessary repairs or replacements to resolve the problem.
Importance of Safety When Working with Electrical Systems
Working with electrical systems, including RV Air Conditioning Wiring Diagrams, requires caution and adherence to safety practices:
- Always disconnect the power source before working on any electrical components.
- Use insulated tools and equipment to prevent electric shocks.
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions to minimize the risk of electric shock.
- If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with electrical work, seek help from a professional mechanic or electrician.
Rv Air Conditioning Wiring Diagram
️Advent Rv Air Conditioner Wiring Diagram Free Download| Gmbar.co

Carrier Rv Air Conditioner Wiring Diagrams Online – Orla Wiring

Dometic Air Conditioner Wiring Schematic
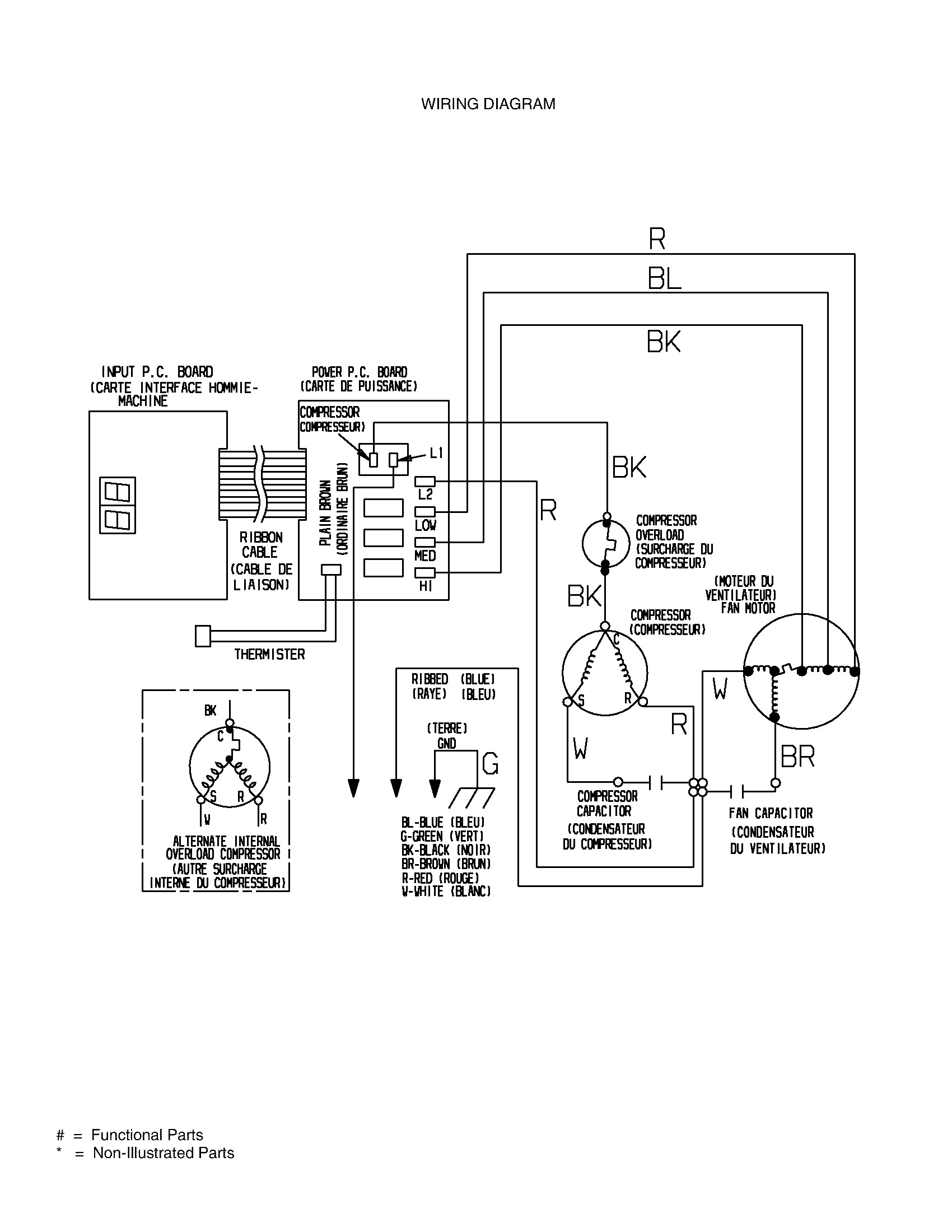
Air Conditioner Wiring – Split Air Conditioner Wiring Diagram

Rv Air Conditioner Wiring Diagram Database

Wiring Rv Air Conditioner